
While this method can lead to a more accurate reflection of service costs, it also requires careful consideration of how to define and measure service units or projects for cost allocation purposes. Variable costing, on the other hand, includes all of the variable direct costs in the cost of goods sold (COGS) but excludes direct, fixed overhead costs. Absorption costing is required by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for external reporting.
Common Absorption Costs Found in Manufacturing Businesses
This treatment aligns the recognition of costs with the revenue generated from the sale of goods, providing a matching principle that is fundamental to accrual accounting. The direct correlation between production levels and variable costs also aids in cost control and management, as it becomes easier to monitor changes in costs in response to changes in production volume. Because absorption costing includes fixed overhead costs in the cost of its products, it is unfavorable compared with variable costing when management is making internal incremental pricing decisions.
What Are the Purposes of Budgeting?
Companies must choose between absorption costing or variable costing in their accounting systems, and there are advantages and disadvantages to either choice. Absorption costing, or full absorption costing, captures all of the manufacturing or production costs, such as direct materials, direct labor, rent, and insurance. Absorbed cost, also known as absorption cost, is a managerial accounting method that includes both the variable and fixed overhead costs of producing a particular product. Knowing the full cost of producing each unit enables manufacturers to price their products. The main advantage of absorption costing is that it complies with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), which are required by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Managerial Accounting
- The method’s adaptability allows it to be tailored to the specific needs of different industries, from manufacturing to services and retail.
- The following subsections delve into how absorption costing is utilized within these diverse business environments.
- Further, the application of AC in the production of additional units eventually adds to the company’s bottom line in terms of profit since the additional units would not cost the company an additional fixed cost.
- In absorption costing, fixed costs such as rent, salaries, and utilities are allocated to products along with variable costs.
- The adoption of absorption costing has direct implications for a company’s tax liabilities.
When we prepare the income statement, we will use the multi-step income statement format. The service sector presents a different set of challenges for absorption costing due to the intangible nature of its products. Unlike manufacturing, where physical goods are produced, service-based companies may not have traditional inventory.
In simple terms, “absorption costing” refers to adding up all the costs of the production process and then allocating them to the products individually. This method of costing is essential as per the accounting standards to produce an inventory valuation captured in an organization’s balance sheet. Variable costing is more useful than absorption costing if a company wishes to compare different product lines’ potential profitability. It is easier to discern the differences in profits from producing one item over another by looking solely at the variable costs directly related to production. The main idea and intention behind using such a absorption costing method for costing purpose is to imply that a product, when produced, absorbs both fixed and variable cost up to a certain extent. It does not depend on the fact that the unit of the product has been sold or it is still lying in the storage as inventory or finished product ready to be sold.
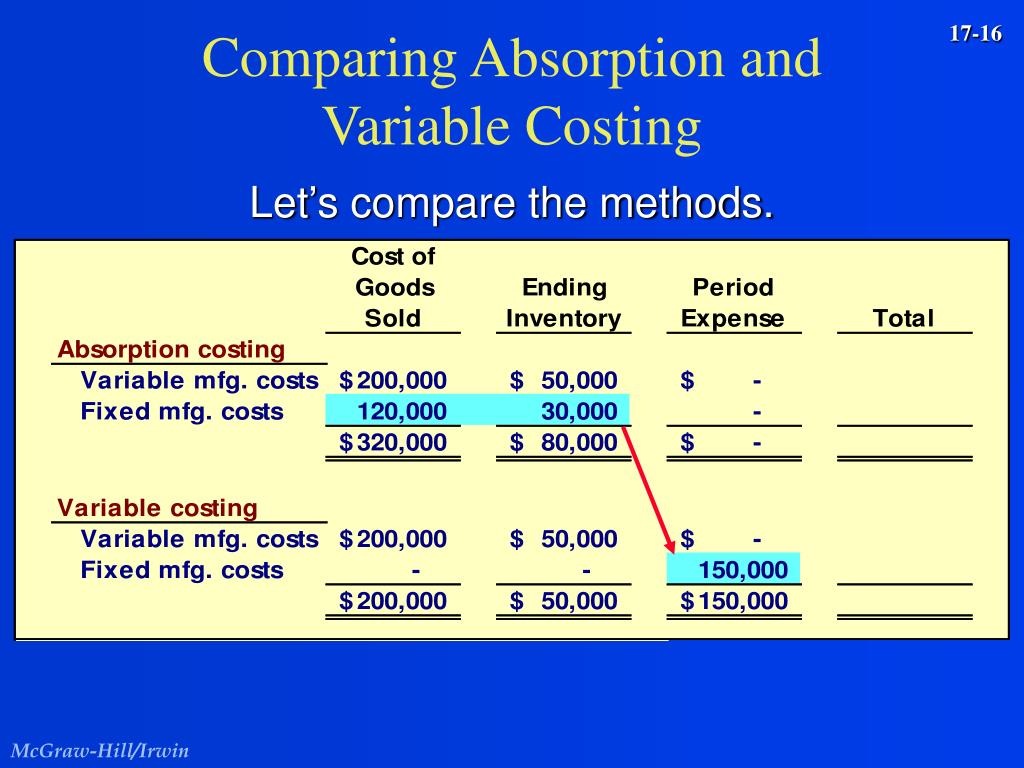
Fixed manufacturing overhead costs are indirect costs and they are absorbed based on the cost driver. In addition, the use of absorption costing generates a situation in which simply manufacturing more items that go unsold by the end of the period will increase net income. Because fixed costs are spread across all units manufactured, the unit fixed cost will decrease as more items are produced. Therefore, as production increases, net income naturally rises, because the fixed-cost portion of the cost of goods sold will decrease. We will use the UNITS SOLD on the income statement (and not units produced) to determine sales, cost of goods sold and any other variable period costs. We will use the UNITS SOLDon the income statement (and not units produced) to determinesales, cost of goods sold and any other variable period costs.
Therefore, fixed overhead will be allocated by $ 1.50 per working hour ($ 670,000/(300,000h+150,000h)). Since this method shows lower product costs than the pricing offered in the contract, the order should be accepted. You should charge sales and administrative costs to expense in the period incurred; do not assign them to inventory, since these items are not related to goods produced, but rather to the period in which they were incurred.
However, ABC is a time-consuming and expensive system to implement and maintain, and so is not very cost-effective when all you want to do is allocate costs to be in accordance with GAAP or IFRS. The absorbed-cost method takes into account and combines—in other words, absorbs—all the manufacturing costs and expenses per unit of a produced item, ones incurred both directly and indirectly. Some accounting systems limit the absorbed cost strictly to fixed expenses, but others include costs that can fluctuate as well. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs remain constant regardless of the level of production. These include expenses like rent for the manufacturing facility, depreciation on machinery, and salaries of supervisors.
Absorption costing is the accounting method that allocates manufacturing costs based on a predetermined rate that is called the absorption rate. It helps company to calculate cost of goods sold and inventory at the end of accounting period. The term absorption costing refers to the method in which the entire production cost is allocated to each and every output proportionately. It is a very common method used widely in the business especially in the manufacturing sector, and in this way the company is able to determine the cost of individual product and services. It is possible to use activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate overhead costs for inventory valuation purposes under the absorption costing methodology.
Yes, you will calculatea fixed overhead cost per unit as well even though we know fixedcosts do not change in total but they do change per unit. When we prepare theincome statement, we will use the multi-step income statementformat. 11 tips to manage your small business finances fails to provide as good an analysis of cost and volume as variable costing. If fixed costs are a substantial part of total production costs, it is difficult to determine variations in costs that occur at different production levels. This makes it more difficult for management to make the best decisions for operational efficiency.
The importance of absorption costing extends beyond mere compliance with accounting standards; it shapes how companies perceive their costs and profits. It also plays a critical role in inventory management, potentially affecting an organization’s financial health and operational strategies. The absorbed cost is a part of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), and is required when it comes to reporting your company’s financial statements to outside parties, including income tax reporting.
